Welcome
Fungi are everywhere around us; they are the most abundant form of life on the planet, counting about 12 million species worldwide. Only a small fraction of them cause disease in humans, but they are responsible for about a billion infections each year. At the same time, new fungi pathogenic to humans are emerging (such as Candida auris, the azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus, etc.) due to climate change and new environmental conditions.
Fungal infections are responsible for more than 1.5 million deaths each year, mostly in immunocompromised patients, while affecting the lives of many millions more. However, they remain a neglected topic by public health authorities, even though most deaths from fungal infections are preventable. It was not until October 2022 that the World Health Organization published the first list of priority fungal pathogens, to increase global interest in the infections they cause and their resistance to antifungal drugs.
The aims of the HSoMM are:
- The promotion of Medical Mycology in Greece and abroad.
- The encouragement and reinforcement of all research efforts and studies in Greece regarding prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of fungal infections.
- The collaboration with public and private institutions and organizations in Greece and abroad, for the progress of Medical Mycology.
Case of the month
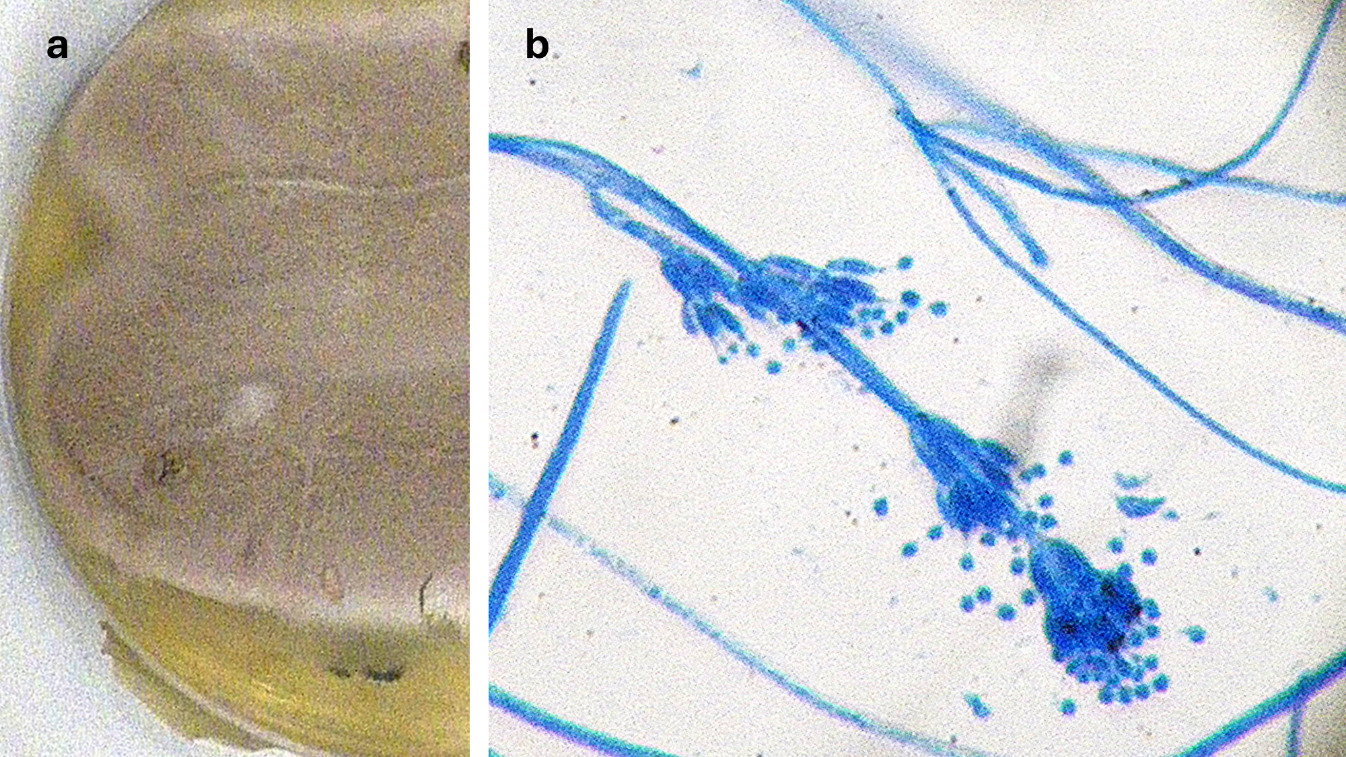
a) Colony on Sabouraud dextrose agar, (b) microscopic morphology of the colony with lactophenol cotton blue, magnification ×400
(Photos: Georgia Vrioni, Department of Microbiology, Medical School, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens)
A 49-year-old man with no significant past medical history presented to the Outpatient Ophthalmology Clinic with an extensive corneal lesion in the left eye. He reported sustaining trauma from an olive tree branch one week earlier during agricultural work. He had been wearing contact lenses for the past 15 years for myopia.
On clinical examination, conjunctival hyperemia and stromal infiltration of the cornea with a discoid yellowish-white appearance were observed.
Direct microscopic examination of corneal scrapings with Gram stain was positive for fungi, while culture yielded a hyaline mold.
Based on the colony morphology on Sabouraud agar (a) and the microscopic features (b), which fungal species is most likely?
1. Aspergillus terreus
2. Purpureocillium lilacinum
3. Penicillium chrysogenum
4. Fusarium solani






